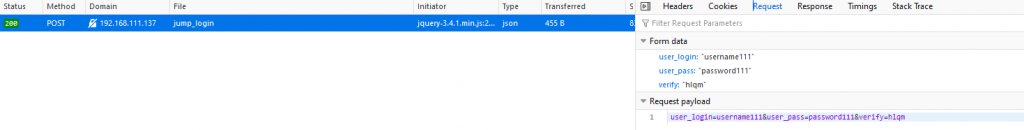
Similarity
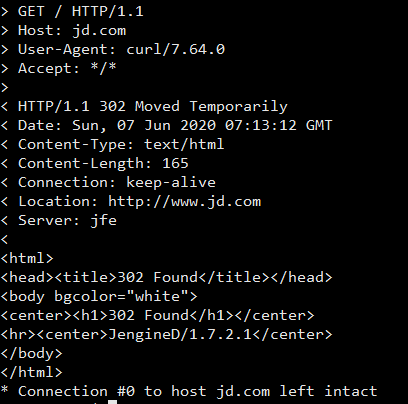
- Both attack techniques rely on the presence of a web cache (e.g., a reverse proxy, CDN, or intermediary caching server) to become effective.
Differences
Target Scope
-
Web Cache Poisoning:
-
- Impacts all users who retrieve content from the poisoned cache. Once a malicious response is stored, every subsequent request served from that cache can deliver the attacker’s payload.
-
Web Cache Deception:
-
- Impacts only a specific victim. The attacker tricks the cache into storing a sensitive, user-specific response and later retrieves it, but the attack must usually be tailored and does not affect other users.
Attack Methodology
-
Web Cache Poisoning:
-
- Involves injecting malicious content (e.g., crafted headers, query parameters) into the cache so that harmful or manipulated data is served to multiple users.
-
Web Cache Deception:
-
- Relies on tricking the cache into storing content it shouldn’t cache (e.g., private pages such as /account or /profile), and then exploiting cache behavior to access sensitive information of a victim. Often requires social engineering or user interaction to trick a specific victim into accessing a crafted URL. For example, the attacker might send a phishing link to the victim, causing their sensitive data to be cached in a publicly accessible locations.
Impact
-
Web Cache Poisoning:
-
- Can be widespread and devastating, enabling mass exploitation.
-
Web Cache Deception:
-
- More targeted and opportunistic, usually focusing on data theft from a single victim rather than large-scale compromise.
Cache Key Manipulation
-
Web Cache Poisoning:
-
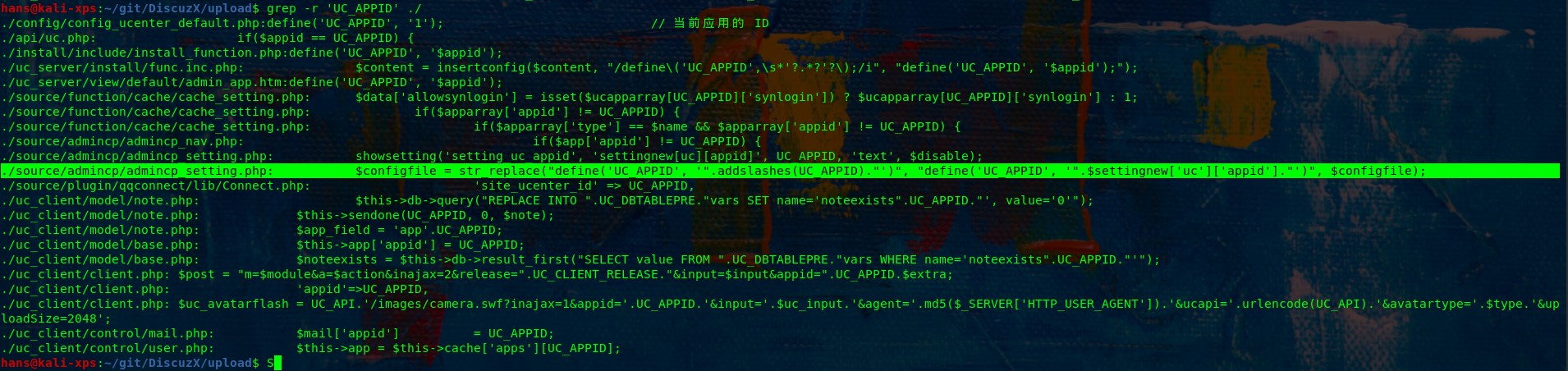
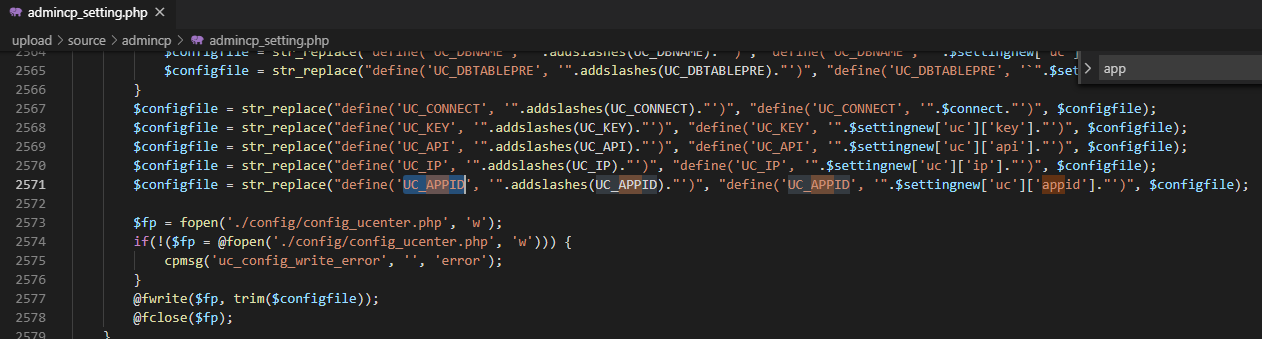
- The attacker manipulates cache keys (e.g., unkeyed headers like
X-Forwarded-Host,Via,Origin,X-Forwarded-Schemeor query parameters likeutm_content) to store a malicious response under a cache key that serves a broad audience. For example, an attacker might exploit a cache that ignores certain headers, allowing a malicious payload (e.g., a script) to be cached for a popular page like /index.html.
- The attacker manipulates cache keys (e.g., unkeyed headers like
-
- Example: An attacker sends a request with a malicious
X-Forwarded-Hostheader, causing the cache to store a response with a malicious JavaScript payload for all users visiting/index.
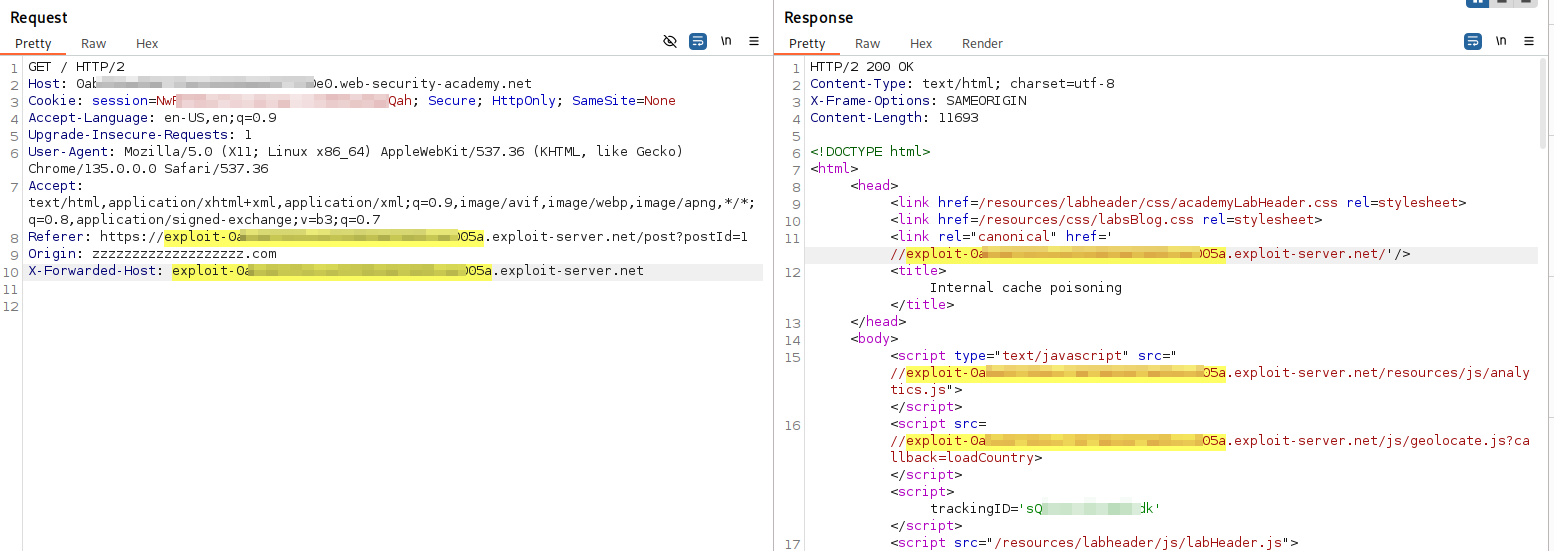
- Example: An attacker sends a request with a malicious
-
Web Cache Deception:
-
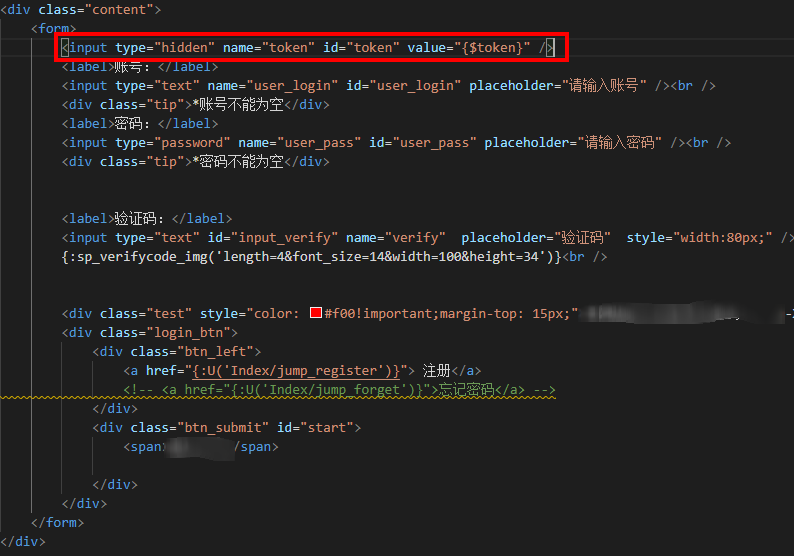
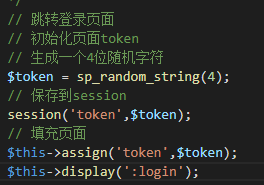
- The attacker tricks the cache into storing a private, user-specific page (e.g., /profile) under a cacheable URL (e.g.,
/scripts/..%2fprofile). If the CDN can configure that caches all path under/scripts/*, and it does not deems..%2fas../, but the origin server will normalizes it, we could send/scripts/..%2fprofileto the victim. When the vimtic open the link, the origin server will return the dynamic profile information of the vimtim, and the CDN will cache it. That is to say we can still user's information by accessing the same URL later.
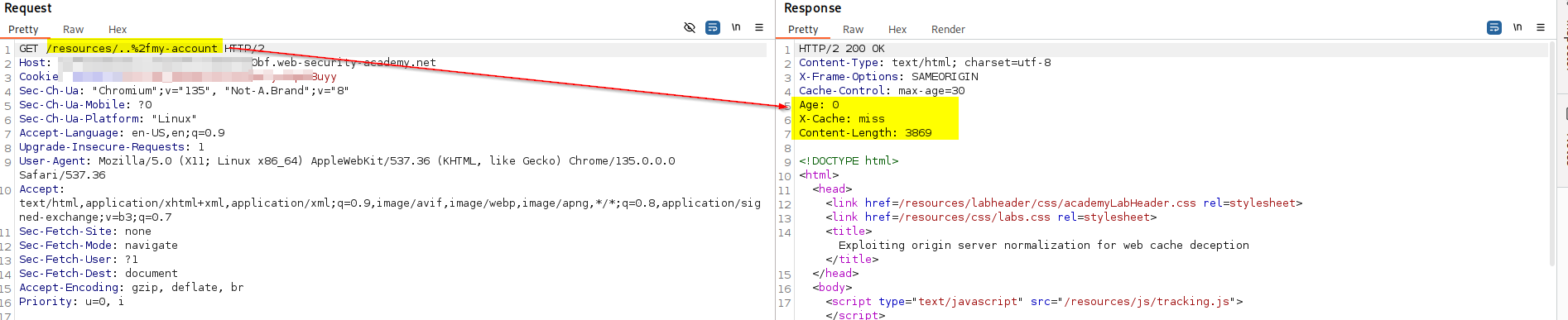
- The attacker tricks the cache into storing a private, user-specific page (e.g., /profile) under a cacheable URL (e.g.,
Source of the Vulnerability
-
Web Cache Poisoning:
-
- The vulnerability is typically in the backend application server. The application improperly trusts and uses unkeyed inputs (like HTTP headers) to dynamically generate the response. The cache simply does its job by storing this maliciously crafted response.
-
Web Cache Deception:
-
- The vulnerability is typically a discrepancy in URL interpretation between the caching layer and the backend server. The cache sees a URL for a harmless, cacheable asset (like a .css or .js file or files under
/scripts/), but the backend server interprets the same URL as a request for a private, dynamic page (like /profile).
- The vulnerability is typically a discrepancy in URL interpretation between the caching layer and the backend server. The cache sees a URL for a harmless, cacheable asset (like a .css or .js file or files under
The Attack Flow
The sequence of events for the attacker is also different.
-
Web Cache Poisoning is a one-step attack for the attacker:
- Attacker sends a crafted request to poison the cache. The attack is now "armed" and waits for victims.
-
Web Cache Deception is a two-step attack for the attacker:
- Attacker tricks a victim into visiting a crafted URL, which causes the victim's private data to be cached.
- Attacker visits that same URL to retrieve the cached data.